Section of research
Within Department of the Research and Development , Divisions are set up, and Sections are located below them.
- Division of Medicinal Resources
- Division of Bioscience
- Division of Complex Biosystem Research
- Division of Presymptomatic Disease
- Division of International Cooperative Research
Division of Medicinal Resources

Section of Medicinal Resource Science
This section analyzes medicinal plants from Asia focusing on genetic, chemical and pharmacological diversity, aiming at the sustainable use of crude drug resources. Those knowledges are applied for developing alternative crude drugs, efficient usage of crude drugs and promotion of cultivation of excellent medicinal plants. Especially, medicinal plants applicable for aging-related diseases and preventive and preemptive medication are focused, we will establish the basis of quality assurance to make them into medicines and cultivate the crude drugs to link them to domestic crude drug production.

Section of Natural Products & Drug Discovery
This section focuses on advanced natural products and attendant drug discovery. We utilize the cutting-edge technologies, such as enzyme engineering, X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, etc. to understand the fundamentals of natural product biosynthesis, the discovery of bioactive compounds, and clarify their molecular mechanism for drug development against various diseases.
Division of Bioscience
Section of Neuromedical Science
This section has progressed studies aiming to overcome neurodegenerative diseases and aging-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, spinal cord injury and sarcopenia, etc. For development epochmaking pharmacotherapies and finding critical regulating factors against neurodegenerative diseases, we investigate them by multi-view points such as pharmacological, neuroscientifical and traditional medicinal approaches. This section covers from basic researches to clinical studies for advancing societal implementation,
Section of Host Defences
This section focuses on understanding the biological defence system including immune response, inflammation, and cellular metabolism, and its role in pathological diseases. We mainly study the effects of natural medicines including Kampo medicines on the biological defence system and extend to drug discovery or system biology approach.
Division of Complex Biosystem Research
In this field, we comprehensively analyze big data obtained from comprehensive analysis (omics analysis) and elucidate new pathological mechanisms. Based on the results, we will make full use of the latest analysis methods from the cell level to the mouse level, and aim to construct a therapeutic strategy for disease state improvement.
Division of Presymptomatic Disease
The pre-disease state, which is known as Mibyou in traditional Japanese medicine (Kampo medicine), is an Oriental medical concept and has still not been scientifically understood. In collaboration with our division and Research Center for Pre-Disease Science, University of Toyama, we are conducting research to scientifically detect the Mibyou state and to clarify the biological meaning of it. Based on the results of the research, we will work on drug development for Mibyou, and consequently the construction of novel medical strategies.
Division of International Cooperative Research
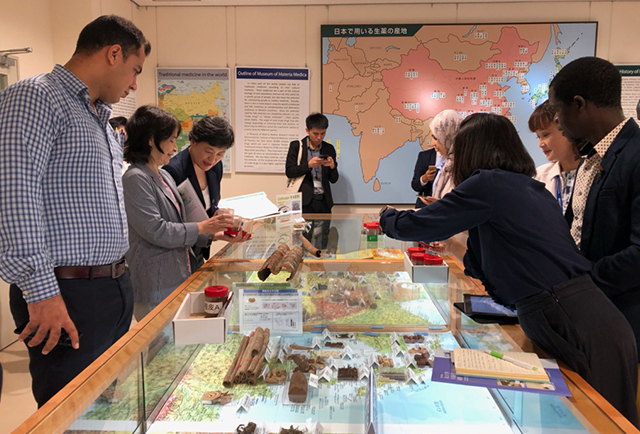

Despite significant progress in the modern western medicine, many diseases have still no appropriate therapy. So there are great expectations for the research outcomes and clinical effects. It requires the current methodologies and the exchange of information about traditional medicines to maintain and develop the researches on traditional medicine at a high level.
In order to facilitate the development of joint scientific programs and research activities, the Institute Natural Medicine has established International Cooperative Center (ICC) in 4 universities of 3 countries, and has made academic exchange and cooperation agreements with 16 foreign institutions of 8 countries.








